Diabetic Kidney Disease
What is diabetic kidney disease?
Diabetic kidney disease, also known as diabetic nephropathy, is a kidney disease caused by diabetes. Diabetic kidney disease is a constantly progressive disease with minimal manifestations in the early stages and it could be much more serious over time. Diabetes causes damage to small blood vessels in the body. Blood vessels are important as they transport nutrients and oxygen for our organs, tissues and cells to live. So when these blood vessels get injured, they can’t perform this function well, which over time, causes damage to our organs.
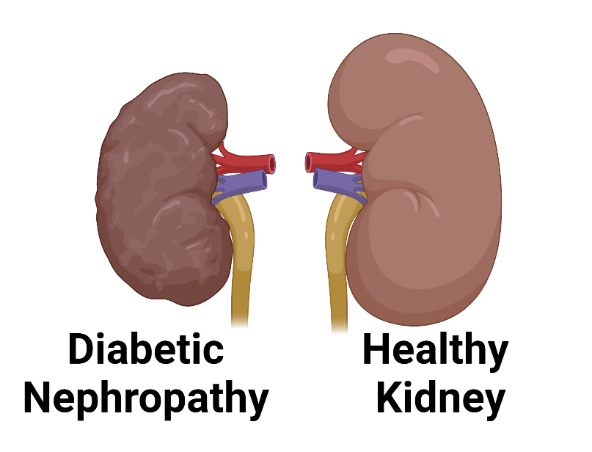
The main function of our kidneys is filtering unwanted by-products and excess water for excretion through the urine. When the blood vessels in the kidneys are damaged due to long-term, uncontrolled or undiagnosed diabetes, it can cause the retention of water, salt and other waste products inside the body.
As diabetes also damages the nerves, people with diabetes may have difficulty emptying their bladder that could eventually lead to urinary tract infections and eventually, kidney damage.
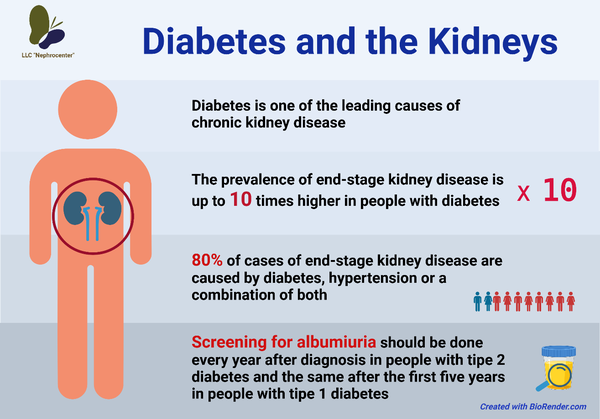
Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney disease. About 1 out of 3 adults with diabetes has kidney disease.
What increases my chances of developing diabetic kidney disease?
Prolonged diabetes increases the likelihood of kidney damage. If you have diabetes, you are more likely to develop kidney disease. Factors that increase the risk of diabetic kidney disease include:
- hypertension
- uncontrolled blood sugar
- long-term diabetes
- overweight (high body mass index)
- malnutrition
- inactive lifestyle
- other complications of diabetes (for example, diabetic polyneuropathy or diabetic eye disease)
- smoking
- heart disease
- family history of diabetes and/or renal failure.
How can I know if I have diabetic kidney disease?
Most people with diabetic kidney disease do not have symptoms. The only way to know if you have diabetic kidney disease is to get your kidneys checked. To diagnose diabetic kidney disease, doctors use simple blood and urine tests. Blood tests to check glucose and kidney function help doctors monitor and determine if your kidneys are suffering from diabetes and to what extent. That's why it's important to make sure you have routine blood tests prescribed by your doctor. Kidney damage can be diagnosed by a simple urine test that can help determine the presence of proteins. The test is very important as, the presence of proteins in urine is the first indication that your kidneys are not functioning correctly. Blood tests to check kidney function also help doctors monitor and determine if your kidneys are affected by diabetes, and by how much. This is why it is important to ensure you go for the scheduled blood tests as prescribed by your doctor. You should get tested every year for kidney disease if you have type 2 diabetes or have had type 1 diabetes for more than 5 years.
How will I know if diabetes is affecting my kidneys?
Signs and symptoms of DKD depend on how badly the kidneys are affected. They include:
- protein in the urine
- high blood pressure
- ankle and leg swelling
- urinating more frequently at night
- abnormal kidney function tests
- nausea and vomiting
- weakness
- anemia
- itching.
How can I keep my kidneys healthy if I have diabetes?
The best way to slow diabetic kidney disease is to try to reach your blood glucose and blood pressure goals. A healthy lifestyle and taking your medicines as prescribed can help you achieve these goals and improve your health overall.

Achieving the target blood glucose level.
Your doctor will check your glycosylated hemoglobin level that is a blood test that shows your average glucose level over the last 3 months. The test is different from your usual blood glucose measurement, which you can do yourself. The target glycosylated hemoglobin level for many people with diabetes is less than 7%. Reach its target level will help you protect your kidneys.
Blood pressure control.
Hypertension causes your heart to work too hard, which can lead to heart attack, stroke and kidney disease. The target blood pressure level for most people with diabetes is below 140/90 mm Hg. Medicines that lower blood pressure can also help slow kidney damage. Two types of blood pressure medicines, ACE inhibitors and ARBs, play a special role in protecting your kidneys. Each has been found to slow kidney damage in people with diabetes who have high blood pressure and diabetic kidney disease. ACE inhibitors and ARBs are not safe for pregnant women.
Develop and/or maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Healthy lifestyle habits can help you reach your target blood glucose and blood pressure levels. Following these steps will also help you maintain good kidney health:
- Stop smoking
- Follow your diet and limit salt and sodium
- Make physical activity a part of your daily routine
- Achieve a healthy body weight
- Get enough sleep. Try to sleep 7-8 hours every night.
Taking medication as prescribed.
Medicines can be an important part of your treatment plan. To help you reach your target blood glucose and blood pressure levels, your doctor may prescribe medications according to your individual needs. You may need to take several medications to control your blood pressure.