Salt and Kidney Disease
How does dietary salt influence my health?
You have probably heard that eating too much salt is bad for your blood pressure. This is because salt contains sodium, and too much sodium makes your body hold onto water. Sodium is important for controlling your blood pressure, but you need the right amount.
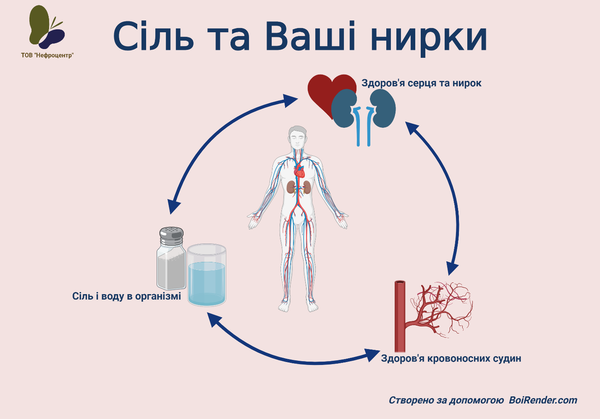
If you eat too much salt, the extra water in your blood means there is extra pressure on your blood vessel walls, raising your blood pressure. If you already have high blood pressure, too much salt will raise it further and may mean that any blood pressure medicines you’re taking don't work as well as they should.
However, eating too much salt can lead not only to hypertension but to all health problems, including heart and kidney disease, obesity, osteoporosis, gut dysbiosis, stroke, and some types of dementia.
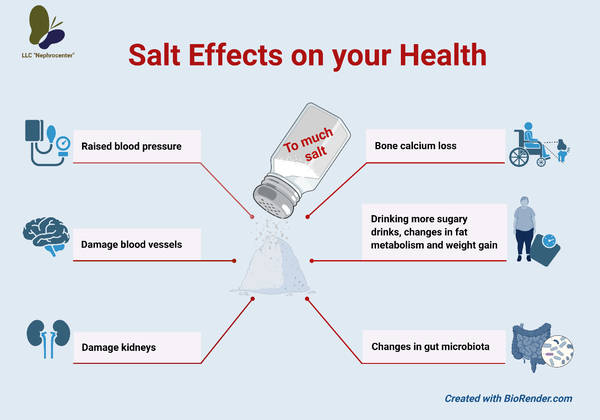
If you have chronic kidney disease, your kidneys can not remove excess salt and fluid so they build up in your body and can cause:
- High blood pressure
- Swelling of ankles, feet, hands, and puffiness under your eyes
- Shortness of breath.
Cutting down on salt is one of the simplest ways to lower your blood pressure, and will start to make a positive difference quickly.
Low Sodium Diet for Kidney Disease
A low-sodium diet is the basis of healthy eating for almost every health condition that affects the kidneys. People with chronic kidney disease, polycystic kidney disease, glomerulonephritis, and/or nephrotic syndrome, and urolithiasis should avoid excessive salt intake. A high-salt diet can cause high blood pressure, which is bad for the kidneys. In fact, high blood pressure is the second leading cause of chronic kidney disease worldwide. In addition, a high-salt diet can worsen uncomfortable edema or water retention for people with kidney disease. For most people, a healthy daily sodium goal is 1,500-2,300 mg per day. Only 1 teaspoon of salt has around 2,300 mg of sodium. This is less than half of what most people eat every day!
How much salt is too much?
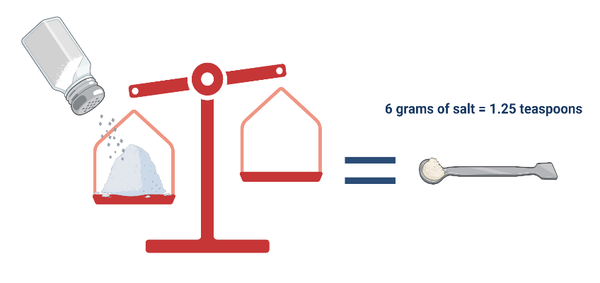
Adults should eat less than 6g of salt a day. This is equal to just over one teaspoon of salt, but most of us eat much more. Most of the salt we eat is hidden in the foods we buy ready-made, like bread, biscuits, breakfast cereals, sauces and condiments, as well as ready meals and takeaways. This hidden salt accounts for around three-quarters (75%) of the salt we eat, only a small amount comes from the salt we add while cooking or at the table.
Some simple ways to reduce salt in your diet
People with or considered at risk of kidney disease or arterial hypertension should ensure that they keep their salt intake below the recommended maximum of 6g. This can be achieved by simple changes, such as:
- Eat only small amounts of high salt foods
- Eat fresh foods like fruit, vegetables, legumes, and wholegrain bread and rice
- Use more herbs and spices
- Read food labels for sodium: use food labels to choose the lowest salt products
Some information about reading labels
Look for sodium on food labels and compare similar products. Always look at the per 100g column as serving sizes will vary. 1g of sodium is the same as 2.5g of salt.
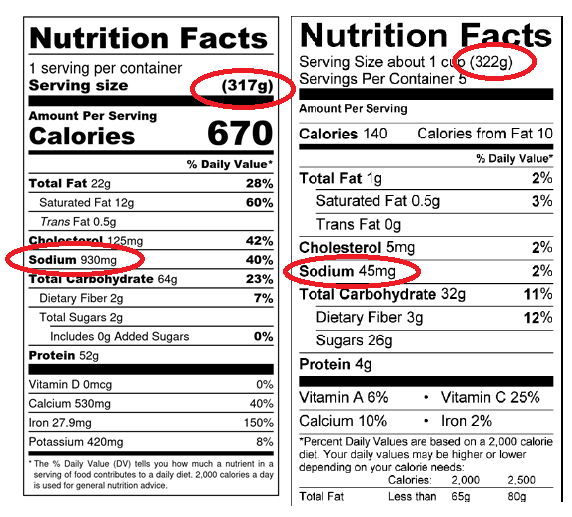
Follow these guidelines to choose lower sodium (and salt) foods.
- Low – 0.1g sodium or less per 100g - Eat plenty of these
- Medium – 0.1-0.6g sodium per 100g - These are usually fine to eat, but choose low salt options where you can
- High – 0.6g sodium or more per 100g - Try to avoid these or eat them only occasionally.
References: