What tests are used for screening and monitoring chronic kidney disease?

For kidney disease, it is sufficient to perform 2 tests:
- Blood analysis for creatinine concentration to calculate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which checks how well your cells filter blood
- Urine analysis for albumin. Albumin is a protein that enters the urine in case of kidney damage
Creatinine
Creatinine is the final product of the normal destruction of your body muscles. Your kidneys remove creatinine from your blood. As kidney disease worsens, creatinine levels increase. With a certain amount of creatinine in blood, your doctor will calculate the GFR.
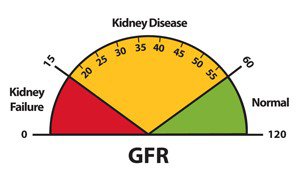
Test results will mean the following:
- GFR greater than 60 mL/min/1/73 m2 is within the normal rate
- GFR less than 60 mL/min/1/73 m2 might indicate kidney disease. Consult your nephrologist about keeping your kidneys healthy at the same
- GFR of 15 or less is referred to as the terminal stage of chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. Most people below this level of GFR will require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Albumin in urine.
Albumin is a protein found in your blood. Healthy kidneys don’t let albumin into your urine. The smaller the albumin level in the urine, the better. Albumin in the urine is called albuminuria. The albumin to creatinine ratio measures in urine samples. This test allows you to estimate how much albumin will be released into your urine within 24 hours.
Test results are:
- 30 mg/g or less is a good result
- More than 30 mg/h may indicate kidney disease
If you have albumin in your urine, the doctor can ask you to repeat the urine test once or twice to confirm the results. The level of albumin in the urine, which remains constant or decreases, may indicate the effectiveness of the proposed treatment.