What is dialysis?

Dialysis is an artificial replacement for kidney function loss as a result of renal failure. The term «dialysis» derives from the Greek word «dialysis», which means distribution and dissolution. During dialysis, the blood is purified from a range of molecules. Molecules are transported on the principle of diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration.
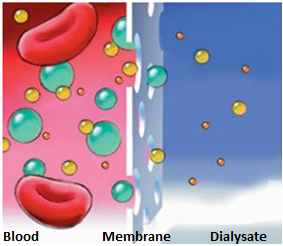
Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of dissolved substances from a solution with the highest concentration thereof into a solution with a lower concentration thereof until equilibrium is reached. Diffusion is based on both peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis. The removal of blood products and electrolytes from the body is ensured by passing them through the membrane to the dialysis solution. By diffusion, small molecules are mostly removed. During peritoneal dialysis, only molecules the size of which does not exceed the peritoneal membrane are moved into the dialysis solution. Depending on the different concentrations, molecular transport
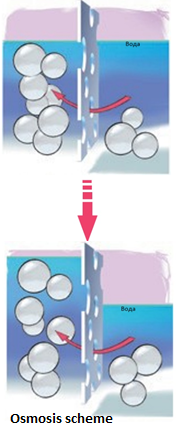
Osmosis
Osmosis is the transfer of water through a semipermeable membrane from a region with a low dissolved substance concentration to an area with a high dissolved substance concentration. In the case of peritoneal dialysis, the dissolved substance, or osmotic agent, is usually glucose. If the same concentration of the substance (diffusion) or osmotic agent (osmosis) is reached on both sides of the membrane equilibrium or saturation occurs. In such a case, there is no further net transfer of dissolved substances or water.
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration is the removal of excess water from the body. During peritoneal dialysis, it is achieved by dialysis solution containing glucose. Dialyzing solutions contain different glucose concentrations. The higher the glucose concentration, the more excess liquid is removed.
Remember that dialysis partially replaces damaged kidney functions such as removal of metabolic products from blood, regulation of water and electrolyte balance, and support of acid-alkali equilibrium. However, the kidneys also perform other functions that cannot replace dialysis therapy, so patients are given additional medication and diet.